Different Colors of Red Wine: Pinot Noir!
Red wine’s color varies due to several elements including grape variety, aging process, and winemaking techniques.
For instance, young red wines usually have a bright, deep color while older ones tend to be lighter. Grape type also plays a role, with certain varieties producing darker wines than others.
The world of red wine is an enchanting spectrum of colors, each hue telling a unique story about its origin, age, and the type of grape used in its creation.
The Science of Red Wine Color
The science of red wine color has been studied extensively over the past few decades.
- The color of red wine is primarily derived from the grape skins, which contain natural pigments known as anthocyanins.
- These compounds are responsible for the varying shades of red, from light ruby to deep purple, found in different red wines.
- The color development during winemaking is a complex process influenced by factors such as grape variety, ripeness, winemaking techniques, and aging.
- Additionally, the interaction between anthocyanins and other compounds, such as tannins, further impacts the final color profile of the wine.
Understanding the science behind red wine color not only enhances our appreciation of its aesthetic qualities but also provides valuable insights for winemakers seeking to innovate and refine their craft.
Factors Affecting Red Wine Color
Understanding the factors that influence red wine color is essential for winemakers seeking to achieve specific shades and hues in their wines, as well as for consumers interested in discerning the subtle nuances of different varieties.
- The primary factors affecting red wine color include grape variety, ripeness at harvest, winemaking techniques, and aging.
- The grape variety plays a significant role, with thicker-skinned varieties generally producing darker, more intense colors.
- The level of ripeness at harvest influences the concentration of color compounds in the grape skins, impacting the wine’s final color.
- Winemaking techniques such as maceration time, fermentation temperature, and use of oak can also affect the color.
- Additionally, the aging process, whether in stainless steel, concrete, or oak, can further modify the wine’s color.
Understanding these factors allows for the creation of diverse and vibrant red wine colors. Moving on to the discussion of common red wine color descriptors… These descriptors often include terms like ruby, garnet, and violet, each providing insight into the wine’s age and grape variety. Additionally, it’s important to consider what colors pair well with wine red, as this knowledge can enhance the overall dining experience when selecting complementary foods and settings. Exploring these pairings adds another layer of appreciation to the enjoyment of red wine.
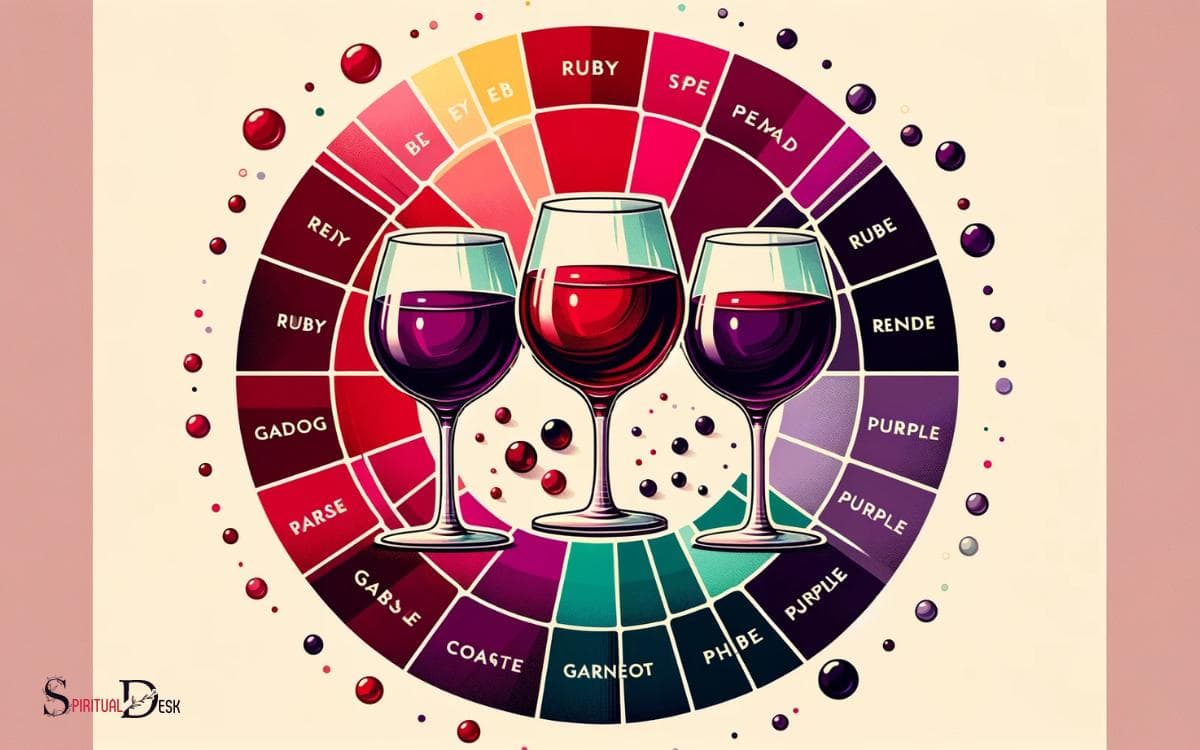
Common Red Wine Color Descriptors
Factors affecting red wine color, such as grape variety, ripeness at harvest, winemaking techniques, and aging, lead to a diverse range of common red wine color descriptors used to characterize the appearance of different wines.
The table below illustrates some of the common red wine color descriptors:
| Descriptor | Description |
|---|---|
| Ruby | Bright red with a hint of blue or purple |
| Garnet | Medium to deep red with brownish hues |
| Crimson | Dark red with a tinge of blue |
| Brick | Reddish-brown, suggesting maturity |
| Magenta | Vivid purplish-red, often associated with young wines |
| Maroon | Deep, rich red with a brownish tinge |
Understanding these descriptors can help enthusiasts and professionals alike to communicate nuances in red wine colors, adding depth to the appreciation and evaluation of these exquisite beverages.
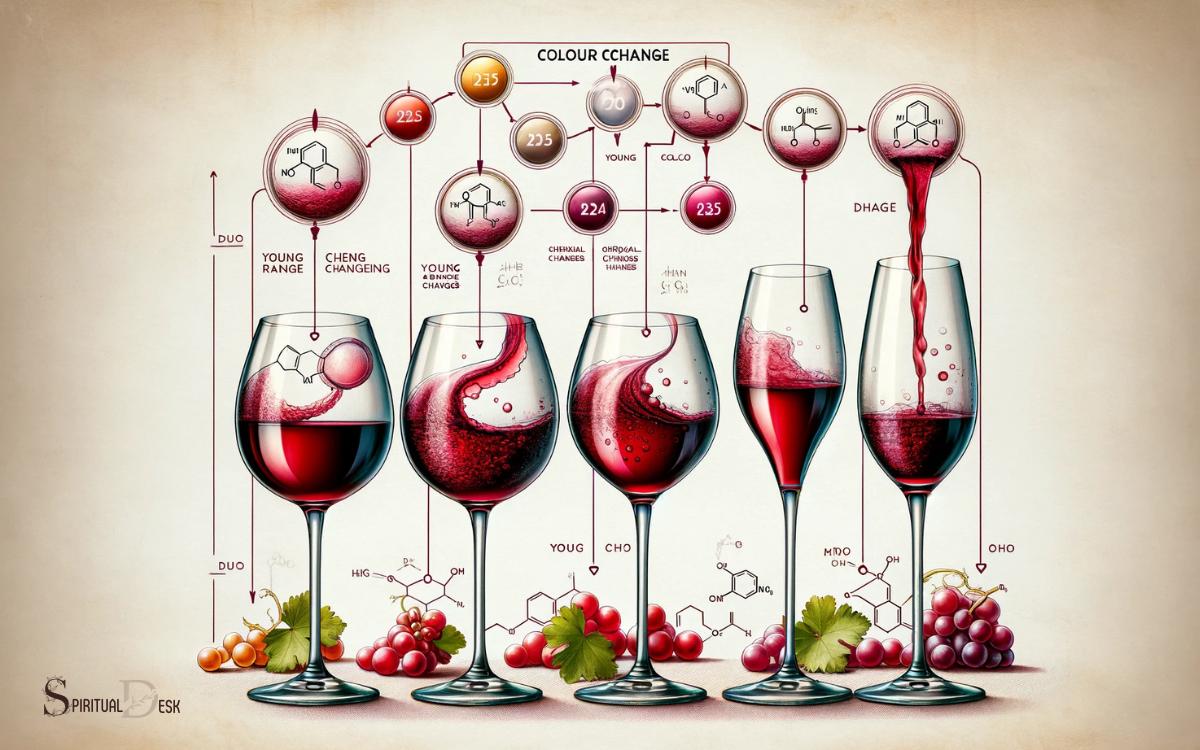
Understanding Red Wine Color Changes
The color changes in red wine are a result of a complex interplay of factors. The aging process can significantly impact the color, as tannins and pigments evolve over time.
Additionally, the type of grape used and environmental influences such as climate and soil composition also contribute to the varying shades of red wine.
Aging Process Effects
The aging process significantly influences the color changes in red wine, impacting its hue, depth, and clarity.
As red wine ages, several factors come into play, altering its appearance and character:
- Oxidation: Over time, the wine’s exposure to oxygen causes the color to shift from a vibrant, youthful red to a more brick-like hue.
- Polymerization: Tannins in the wine bind together, leading to a softening of the color and a more translucent appearance.
- Sedimentation: As the wine matures, pigments and tannins combine to form sediments, affecting both the color and the wine’s stability.
- Acidity Levels: Changes in acidity can impact the overall color profile, with higher acidity often preserving the wine’s red color for a longer period.
Understanding these aging effects is crucial for both wine enthusiasts and producers seeking to appreciate and craft the finest red wines.
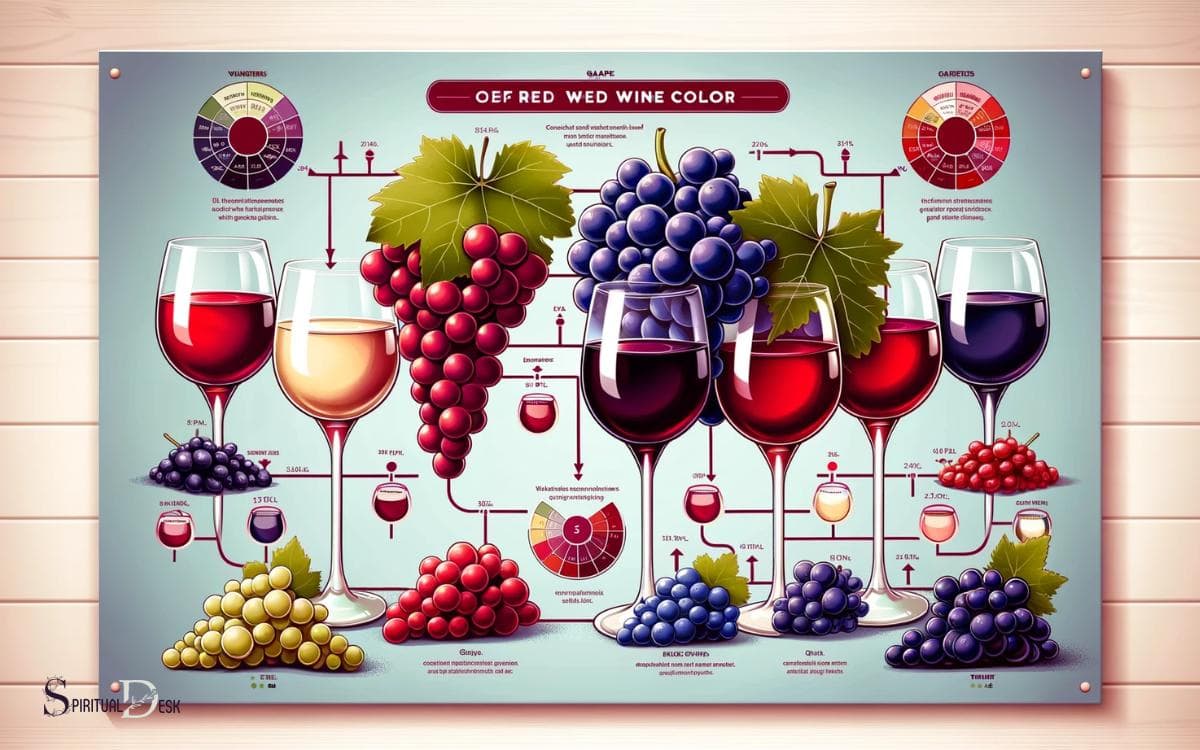
Grape Variety Influences
In understanding red wine color changes, the hue and depth are influenced by the specific grape variety and the region in which it is grown.
Different grape varieties yield varying colors, from deep purple to ruby red and even light garnet.
Below is a table that illustrates the influence of grape varieties on red wine colors:
| Grape Variety | Color Influence |
|---|---|
| Cabernet Sauvignon | Deep red, intense hues |
| Merlot | Ruby red, medium depth |
| Pinot Noir | Lighter garnet, translucent |
The grape variety significantly impacts the color profile of the red wine, offering a diverse range of visual experiences. Understanding these influences fosters a deeper appreciation for the artistry of winemaking.
Environmental Factors Impact
Transitioning from the influence of grape varieties on red wine colors, it is crucial to delve into the impact of environmental factors on these grapes and their resulting hues.
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping the color profile of red wines.
These factors include:
- Sunlight Exposure: Sunlight affects the development of anthocyanins in grape skins, which are responsible for the red color in wines.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Fluctuations in temperature during grape maturation can influence the rate of anthocyanin biosynthesis, affecting the depth and intensity of the wine’s color.
- Soil Composition: The mineral composition of the soil can impact the availability of nutrients to the grapevines, ultimately influencing the color development in the grapes.
- Water Stress: Moderate water stress can lead to a higher concentration of color compounds in the grapes, intensifying the red wine color.
Red Wine Color and Ageing
The color of red wine is a fascinating aspect that evolves with ageing. As red wine ages, its color transforms, providing a visual indicator of the aging process.
Understanding the impact of ageing on the color of red wine can offer valuable insights into the quality and potential flavor profile of the wine.
Red Wine Color Changes
Red wine color changes over time due to chemical reactions and interactions with oxygen, which influence its appearance and character.
These changes are indicative of the wine’s aging process and can provide insight into its quality and flavor profile.
The following factors contribute to red wine color changes:
- Oxidation: Exposure to oxygen causes the wine to darken and lose its vibrancy.
- Polymerization: Tannins and pigments form larger compounds, leading to a shift in color from red to orange or brown.
- Sedimentation: As the wine ages, particles settle, resulting in a clearer appearance.
- Color Evolution: Young red wines tend to have a more purple or ruby hue, while older wines develop a garnet or brick-red color.
Understanding these color changes enhances appreciation for the complexities of red wine and its evolution over time.
Aging Process Impact
The evolution of red wine color and aging progresses through a series of chemical reactions and interactions with oxygen, contributing to the wine’s overall appearance and quality.
- This transformation is due to the polymerization of tannins and the precipitation of color pigments, resulting in a softer, more orange-toned appearance.
- Additionally, the aging process plays a crucial role in the development of complex aromas and flavors, as well as the refinement of the wine’s texture and structure.
- Oxidative processes during aging can also lead to the formation of sediment, which further impacts the wine’s color and overall sensory profile.
Understanding the impact of aging on red wine color is vital for appreciating the nuances of different vintages and styles.
Color as Indicator
An accurate assessment of red wine color serves as a crucial indicator of its aging process and overall quality.
The color of red wine evolves as it ages, providing valuable insights into its development and potential.
Understanding the relationship between red wine color and aging can significantly enhance appreciation and evaluation of different varietals.
- Hue Variation: The shift in hue from a deep, vibrant red to a more garnet or brick-like color indicates the wine’s maturity.
- Translucency and Viscosity: Changes in translucency and viscosity can reveal the wine’s age and structure.
- Brick Red or Brown Tinges: These can signify extended aging, offering a glimpse into the potential flavor profile and complexity.
- Rim Variation: Observing the color variation at the wine’s rim can provide clues about its age and overall quality.
Red Wine Color and Grape Varieties
When considering red wine color and grape varieties, it is important to understand the relationship between the grape skin pigment and the resulting wine hue.
- Different grape varieties contain varying levels of anthocyanins, which are responsible for the color of red wine.
- For example, Cabernet Sauvignon grapes have thick skins rich in pigment, resulting in a deep, opaque red wine.
- In contrast, Pinot Noir grapes have thinner skins with less pigment, producing a lighter, translucent red wine.
- Additionally, factors such as climate, soil, and winemaking techniques also influence the final color of the wine.
- Winemakers are constantly innovating to create new and exciting red wine colors, pushing the boundaries of traditional expectations.
Understanding the interplay between grape varieties and wine color opens up a world of possibilities for wine enthusiasts and connoisseurs alike.
Red Wine Color and Food Pairing
Red wine color complements a wide range of foods, enhancing the dining experience with its rich and diverse palette.
When considering food pairing with red wine, it’s essential to take into account the wine’s characteristics, as well as the flavors and textures of the dish.
Here are some innovative red wine and food pairings to elevate your dining experience:
- Light-bodied red wines: Pair with delicate dishes such as grilled salmon or roasted chicken.
- Medium-bodied red wines: Complement these with dishes like pasta with tomato-based sauces or mushroom risotto.
- Full-bodied red wines: These are best paired with rich, hearty dishes such as steak, braised short ribs, or lamb stew.
- Bold and tannic red wines: Match with strong flavored foods like aged cheeses, charcuterie, or barbecued meats.
Conclusion
The science of red wine color is a complex and multifaceted subject, influenced by various factors such as grape varieties, ageing, and food pairing.
Understanding the different colors of red wine and their descriptors is essential for wine enthusiasts and professionals alike.
By exploring the intricate relationship between red wine color and its various influences, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the art and science of winemaking.