Does Red Food Coloring Have a Taste? No!
No, red food coloring does not have a taste.
Red food coloring is a common ingredient used in cooking and baking to provide visual appeal. It is made of synthetic or natural dyes that are approved for food use.
The primary function of this coloring is to make food look more appealing or match certain flavor expectations.
For example, red food coloring might be used in a strawberry cake to give it a more vibrant color.
However, the coloring itself does not have a discernible taste and should not affect the flavor of the food.
Although red food coloring doesn’t have a taste, it can sometimes cause an allergic reaction in some people. This is usually rare, but it’s something to be aware of when using this ingredient.
Key Takeaway
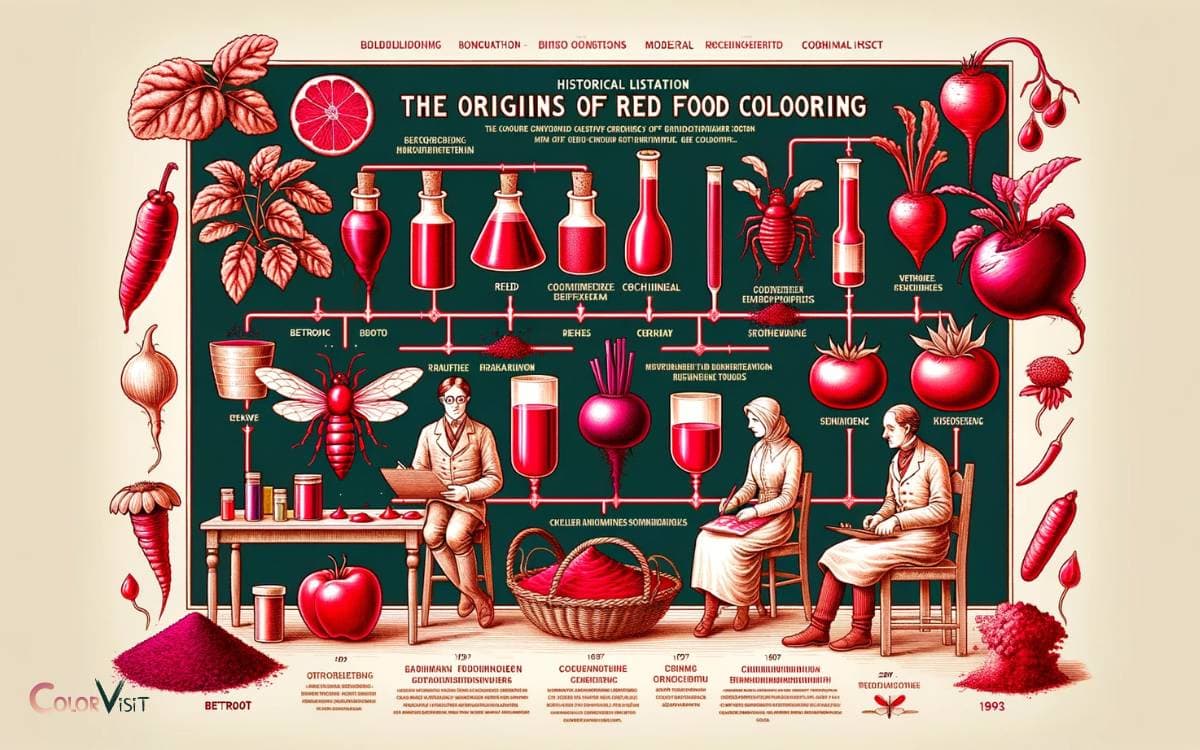
The Origins of Red Food Coloring
Red food coloring, known for its vibrant hue, has its origins in natural sources such as insects, plants, and minerals.
- The use of insects like the cochineal beetle was a common practice in early civilizations. These insects produce carminic acid, which yields a rich red pigment when processed.
- Additionally, certain plant extracts, like those from the vibrant red beet, have been utilized for their natural coloring properties.
- Furthermore, minerals such as cinnabar, a form of mercury sulfide, were historically used to create red pigments.
- Over time, advancements in technology and chemistry have led to the development of synthetic red food dyes, providing innovative alternatives to natural sources.
Today, modern food industry innovations continue to explore new natural and synthetic sources for red food coloring, catering to consumer preferences for clean label, sustainable, and innovative products.
The Chemical Composition of Red Food Coloring
With a molecular structure carefully designed to impart a vibrant red hue, the chemical composition of red food coloring plays a crucial role in the sensory experience of food products.
- Red food coloring is typically made from synthetic dyes such as Red 40 or natural sources like beet juice.
- Red 40, also known as Allura Red AC, is a commonly used synthetic dye composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen molecules.
- It is water-soluble and stable under various pH conditions, making it suitable for a wide range of food and beverage applications.
- On the other hand, natural red food colorings derived from beet juice contain betalains, which are responsible for their red coloration.
- Understanding the chemical composition of red food coloring is essential for creating visually appealing and marketable food products.
This understanding leads us to explore the impact of red food coloring on flavor perception.
The Impact of Red Food Coloring on Flavor Perception
The presence of red food coloring can alter the perceived flavor profile of food products. Research has shown that the visual appearance of food significantly impacts flavor perception.
Red food coloring, in particular, has been found to influence the perception of sweetness and fruitiness in various food items.
This phenomenon can be attributed to the psychological association between the color red and ripe, sweet fruits.
To illustrate the impact of red food coloring on flavor perception, consider the following table:
| Food Product | Without Red Food Coloring | With Red Food Coloring |
|---|---|---|
| Strawberry Yogurt | Mild sweetness | Enhanced sweetness |
| Cherry Flavored Drink | Subtle fruitiness | Intensified fruitiness |
| Red Velvet Cake | Moderate sweetness | Rich, decadent sweetness |
| Tomato Soup | Savory tomato flavor | Perception of added sweetness |
Innovation in food science continues to explore the intricate relationship between color and flavor perception, providing opportunities for creative and impactful product development.
Common Uses of Red Food Coloring in Culinary Applications
A common application of red food coloring in culinary practices is to enhance the visual appeal of various food products.
- This coloring agent is frequently used in baking to create vibrant red velvet cakes, eye-catching red frosting for cupcakes, and visually striking macarons.
- In addition, red food coloring is often utilized in the production of candies, such as gummy bears and hard candies, to provide a bold and consistent red hue.
- Furthermore, it is employed in savory dishes like red pasta, sauces, and marinades to add a visually appealing element to the presentation of the dish.
The versatility of red food coloring allows chefs and home cooks to innovate and experiment with creating visually stunning culinary creations that captivate the senses and elevate the overall dining experience.
Exploring the Misconceptions Surrounding Red Food Coloring
There are misconceptions surrounding the taste of red food coloring, which warrant exploration to clarify its actual flavor profile.
Red food coloring is often mistakenly associated with a specific taste, but it is important to debunk these myths and provide accurate information.
Here are some key misconceptions surrounding red food coloring:
- Red food coloring tastes like strawberries, cherry, or any other red fruit.
- Red food coloring has a bitter or artificial aftertaste.
- Red food coloring alters the taste of the food it is added to.
- Red food coloring is not safe for consumption due to its taste.
Conclusion
Red food coloring does not have a distinct taste, as it is primarily used to enhance the visual appeal of food and beverages.
Its chemical composition and impact on flavor perception play a significant role in the culinary world.
Despite common misconceptions, red food coloring is widely used in a variety of culinary applications, adding vibrancy and aesthetic appeal to a wide range of dishes and drinks.