How do We See the Color Red? Wavelengths!
We perceive the color red through a process involving light, wavelengths, and our vision system.
The light reflected by a red object consists of specific wavelengths absorbed by the cones in our eyes, which send signals to our brain to interpret as the color red.
The process of seeing the color red begins when light hits an object. The object absorbs certain wavelengths of light and reflects others.
For red objects, longer wavelengths are reflected. These reflected wavelengths reach our eyes, where they are absorbed by cones, specialized cells in our retinas that perceive color. These cones send signals to the brain, which interprets these signals as the color red.
The reflected light enters your eyes, is absorbed by the cones, and signals are sent to your brain that you are seeing red.
Understanding the perception of red is essential in fields like marketing and design, where red can evoke strong emotions and responses, making it a powerful tool in visual communication.
Key Takeaway
The Basics of Color Perception
Color perception begins with the interaction between light and the specialized cells in the human eye known as cones.
- These cones are sensitive to different wavelengths of light, allowing us to perceive a spectrum of colors.
- The study of color psychology delves into how different colors can evoke distinct emotional and behavioral responses, influencing perception and cognition.
- Optical illusions further highlight the complexities of color perception, showcasing how our brains can be tricked into seeing colors and shapes that aren’t actually present.
Understanding the basics of color perception is crucial in various fields, from art and design to marketing and branding.
The Role of Light and Wavelengths
The color red is perceived through the interaction of light and the human visual system. Light consists of various wavelengths, and when it interacts with an object, certain wavelengths are absorbed and others are reflected.
These reflected wavelengths enter the eye and are processed by the brain, resulting in the perception of the color red.
Light and Color Perception
Perceiving color involves detecting and interpreting different wavelengths of light.
- These wavelengths are crucial in evoking emotional responses and embodying cultural symbolism. Color vision, a complex process involving the eyes and brain, allows us to perceive and interpret these wavelengths.
- However, individuals with color blindness may experience limitations in differentiating certain colors due to deficiencies in their color-sensing mechanisms.
- The interplay of light and color perception is at the forefront of innovation, as researchers explore new technologies to enhance color vision for those with impairments.
- Understanding the role of light and wavelengths in color perception not only enriches our comprehension of the world around us but also opens doors to innovative solutions that could revolutionize how we perceive and interact with colors in our daily lives.
Wavelengths and Visual Stimuli
When observing the color red, our visual perception is influenced by the interaction of light with our eyes’ photoreceptor cells.
- This interaction is crucial in understanding the role of wavelengths and visual stimuli in color psychology and visual processing.
- The sensory perception of the color red is deeply rooted in the physiological and psychological aspects of color interpretation.
- Wavelengths of light play a significant role in how we perceive and interpret the color red. The specific wavelength of red light stimulates the cones in our eyes, which then send signals to the brain for processing.
This process is integral to our understanding of how the human visual system deciphers and processes the color red, offering valuable insights into the complexities of visual perception and color interpretation.
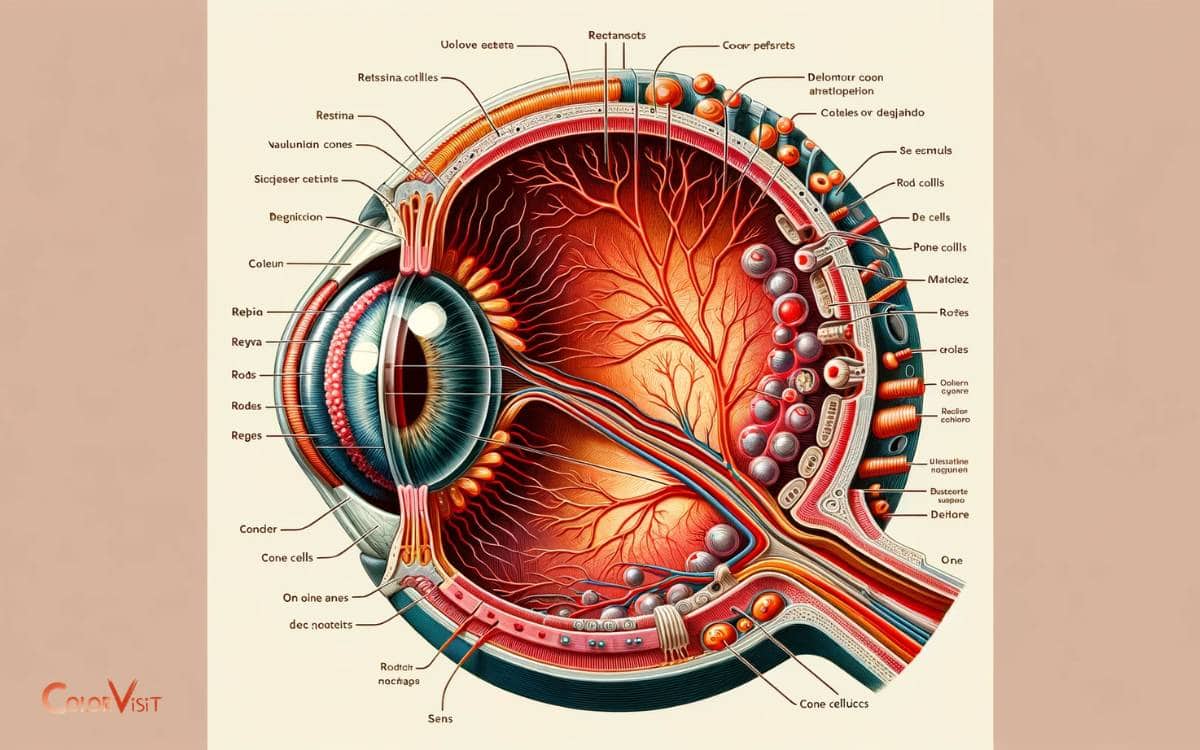
Anatomy of the Human Eye
The human eye’s ability to perceive the color red is a fascinating interplay of retinal physiology and visual perception.
The following key anatomical features contribute to this remarkable ability:
- Cone cells: Specialized photoreceptor cells in the retina, particularly the red cone cells, are specifically sensitive to red light wavelengths.
- Optic nerve: Once the red light is absorbed by the cone cells, the optic nerve transmits this information to the brain for interpretation.
- Retinal layers: The layers of the retina, especially the outer nuclear layer and the retinal pigment epithelium, play a vital role in processing red light and transmitting signals to the brain.
- Fovea centralis: This small, central pit in the retina is responsible for the sharpest vision and plays a crucial role in perceiving red hues.
Evolutionary Significance of Red
The color red holds evolutionary significance as it has been found to attract attention in nature, serving as a warning or a signal of danger.
Additionally, red holds deep cultural symbolism and significance in various societies, often representing emotions such as love, passion, and anger.
Understanding the evolutionary roots and cultural implications of the color red can offer valuable insights into human behavior and perception.
Attracts Attention in Nature
The vibrant color red has long been recognized as a significant attention-grabber in the natural world, with implications for its evolutionary significance.
This visual attraction plays a crucial role in animal behavior and environmental impact, influencing natural selection.
The evolutionary significance of red can be attributed to several key factors:
- Contrast enhancement: Red stands out prominently against various natural backgrounds, making it highly noticeable to organisms.
- Signaling vitality: In nature, red is often associated with ripe fruits, flowers, and healthy individuals, making it an indicator of vitality and desirability.
- Warning signals: Many species utilize red coloration as a warning sign, deterring predators and preventing harm.
- Mating displays: Red serves as a prominent element in mating rituals, attracting potential partners and ensuring reproductive success.
This visual prominence of red in nature has shaped the evolutionary landscape, influencing the survival and reproduction of numerous species.
Cultural Symbolism and Significance
With its evolutionary significance firmly established, red’s cultural symbolism and significance play a crucial role in shaping human perceptions and behaviors.
- Across various cultures, red is laden with symbolism and traditions, often representing power, passion, and vitality.
- Its psychological effects are profound, as studies have shown that exposure to the color red can elicit strong emotional responses, such as increased heart rate and heightened arousal.
- In many Eastern cultures, red is associated with good luck and prosperity, while in Western cultures, it is often linked to danger or romance.
- The cultural significance of red extends to religious and spiritual contexts, where it can symbolize sacrifice, sin, or divine love.
Understanding the diverse cultural interpretations of red provides valuable insights into the complexities of human perception and behavior.
Cultural and Psychological Associations
Cultural and psychological associations with the color red play a significant role in shaping our perceptions and emotional responses.
Understanding these associations can provide insights into the profound impact of this vibrant hue on human cognition and behavior.
- Cultural Significance: The color red holds diverse cultural meanings, symbolizing anything from passion and love to danger and warning, varying widely across different societies and historical contexts.
- Psychological Impact: Red is known to evoke strong emotional and physiological responses, triggering feelings of intensity, excitement, and even aggression. Its effect on human behavior and decision-making processes has been extensively.
- Symbolism and Tradition: In many cultures, red holds deep symbolic value, often representing auspiciousness, vitality, and prosperity, influencing customs and traditions related to events such as weddings, festivals, and celebrations.
- Personal Associations: Additionally, individuals may have personal associations with the color red, based on their unique experiences and memories, further shaping their emotional responses to it.
Impact on Red in Marketing and Design
Exploring the influence of red in marketing and design unveils its powerful impact on consumer behavior and visual communication strategies.
- The color red has a profound psychological impact, evoking strong emotions and driving action.
- In marketing, red is often used to grab attention, create a sense of urgency, and stimulate appetite.
- It can convey excitement, passion, and energy, making it a popular choice for branding and packaging.
- Red is also known to increase heart rate and create a sense of urgency, making it a powerful tool for influencing consumer behavior. In design, red can be used strategically to create focal points, evoke specific moods, and enhance brand identity.
When used thoughtfully, red can leave a lasting impression and elevate the overall impact of marketing and design efforts.
Conclusion
The perception of the color red is a complex process involving light, the human eye, and the brain. Its evolutionary and cultural significance has shaped its psychological associations and impact on marketing and design.
So next time you see the color red, remember that it’s not just a color, but a powerful force with deep-rooted effects on our perception and behavior. Think about that the next time you’re shopping for a new car or choosing a logo for your business.