In Japanese Four O’clock Plants, Red Color Is Incompletely
Japanese Four O’clock plants, also known as Mirabilis jalapa, exhibit a unique trait where the red color in their flowers shows incomplete dominance.
This results in a range of red shades and patterns, often leading to flowers with variegated pigmentation.
The incomplete dominance in Japanese Four O’clock plants is due to the way their genetic makeup influences pigment production.
Factors affecting the red color expression:
Discover the alluring charm of Japanese Four O’clock plants, where genetics paints each bloom with its own brush of red, creating a living tapestry that captivates gardeners and botanists alike.
Key Takeaway
Botanical Characteristics of Japanese Four O’clock Plants
The botanical characteristics of Japanese Four O’clock plants include their distinctive trumpet-shaped flowers and their ability to produce a range of vibrant colors, including the incomplete red coloration that has garnered recent scientific interest.
These plants exhibit a fascinating trait where the red color appears incomplete, leading to a unique visual appearance.
This phenomenon has piqued the curiosity of researchers and botanists, driving innovative studies to understand the genetic and biochemical basis of this intriguing color variation.
The exploration of these botanical characteristics not only contributes to our understanding of plant genetics but also offers potential applications in horticulture and biotechnology.
By delving into the mechanisms behind this incomplete red coloration, there is an opportunity to uncover novel pathways for manipulating color expression in plants, presenting exciting prospects for future research and practical applications.
The Unique Red Coloration Phenomenon
The unique red coloration phenomenon in Japanese Four O’clock plants is a result of a complex interplay of red color genetics and environmental color triggers.
Understanding the genetic basis for the incomplete red coloration in these plants provides insights into their evolutionary advantage and adaptation to their surroundings.
Red Color Genetics
Discussing the unique red coloration phenomenon in Japanese Four O’clock plants involves examining the genetics underlying this distinctive trait.
The red color genetics in these plants are fascinating and complex, contributing to the incomplete red coloration observed.
Understanding the intricate genetic mechanisms governing the red coloration not only sheds light on the biology of Japanese Four O’clock plants. Also presents opportunities for innovative approaches in horticulture and biotechnology.
Further exploration of these genetic intricacies can lead to novel applications and advancements in plant science.
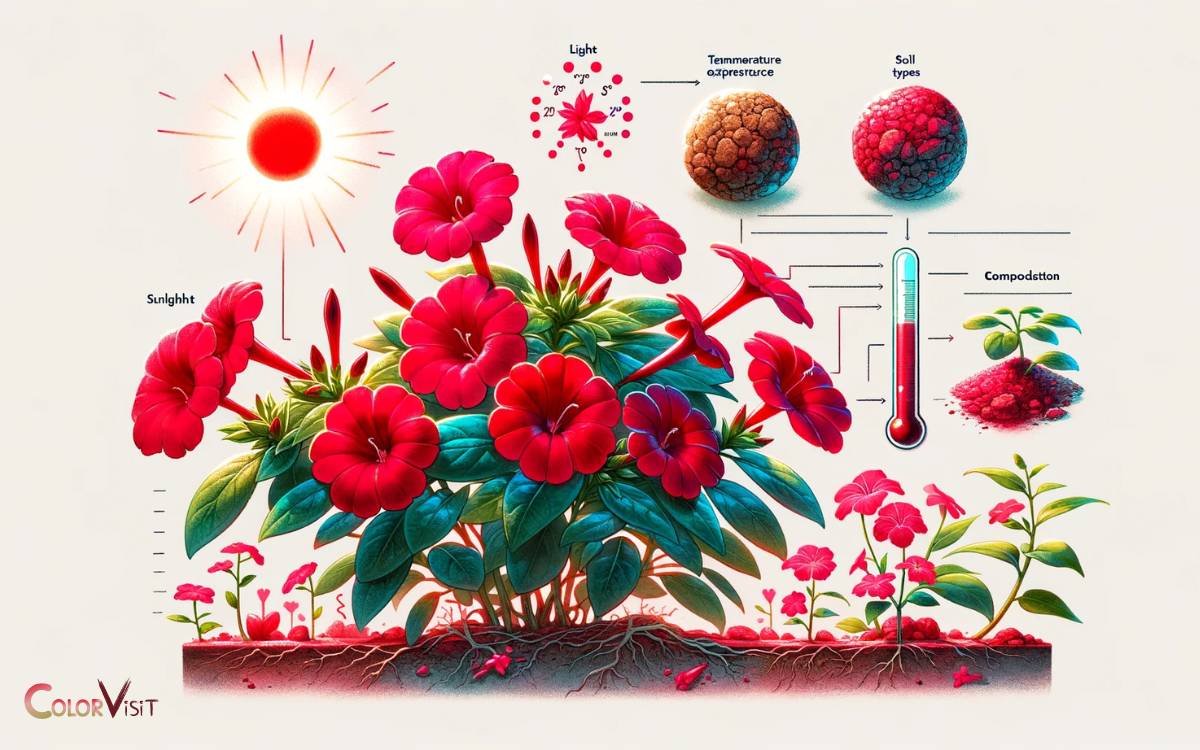
Environmental Color Triggers
The interaction of environmental factors serves as a pivotal influence on the unique red coloration phenomenon observed in Japanese Four O’clock plants.
The expression of the red pigment in the flowers is intricately linked to specific environmental triggers, showcasing a remarkable adaptability and responsiveness within the plant species.
The table below provides a visual representation of the key environmental color triggers that contribute to the distinctive red coloration phenomenon in Japanese Four O’clock plants:
| Environmental Factor | Influence on Red Coloration |
|---|---|
| Light Intensity | Enhances pigmentation |
| Temperature Variations | Induces color development |
| Soil Nutrient Levels | Affects pigment production |
Understanding the intricate interplay between these environmental factors sheds light on the unique red coloration process within the species.
Plant Evolutionary Advantage
An intrinsic evolutionary advantage is conferred to Japanese Four O’clock plants through their adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, as exemplified by the intricate interplay of specific environmental triggers that contribute to the unique red coloration phenomenon.
This adaptive trait provides several advantages to the plant species:
- Enhanced pollinator attraction due to the striking red coloration.
- Increased resistance to environmental stresses such as drought and high temperatures.
- Improved camouflage in specific habitats, offering protection from herbivores.
- Facilitation of efficient light absorption for photosynthesis.
- Promotion of genetic diversity through the transmission of advantageous traits to offspring.
This remarkable interplay of environmental adaptation and survival strategies underscores the significance of the unique red coloration phenomenon in Japanese Four O’clock plants.
Genetic Factors Influencing Red Pigment Development
The development of red pigment in Japanese Four O’clock plants is influenced by genetic factors, particularly red pigment gene mutations.
Understanding the interplay between genetic and environmental influences is crucial to comprehensively unraveling the incomplete red coloration in these plants.
Red Pigment Gene Mutations
Genetic mutations play a crucial role in influencing the development of red pigment in Japanese Four o’clock plants.
These mutations can lead to variations in the expression of red pigment genes, ultimately impacting the plant’s coloration.
The following unordered list illustrates how red pigment gene mutations contribute to the plant’s coloration:
- Introduction of novel color variations
- Alteration of pigment intensity
- Creation of unique color patterns
- Influence on color stability
- Contribution to diverse color combinations
Understanding the effects of these genetic mutations is essential for unlocking the full spectrum of color possibilities in Japanese Four o’clock plants.
Furthermore, it provides valuable insights for breeding programs aimed at enhancing the plant’s ornamental value.
Environmental Impact on Color
Continuing from the previous subtopic, the interplay of genetic factors with environmental conditions significantly shapes the development of red pigment in Japanese Four o’clock plants.
- The expression of genes responsible for red pigment production can be influenced by various environmental factors such as light intensity, temperature, and soil nutrients.
- For instance, studies have shown that higher light intensity tends to enhance the production of red pigments, while certain nutrient deficiencies can limit its development.
- Furthermore, specific genetic mutations may interact differently with environmental cues, leading to variations in the intensity and distribution of red coloration.
Understanding these complex interactions between genetic makeup and environmental influences is crucial for developing innovative strategies to modulate red pigment expression in Japanese Four o’clock plants, with potential applications in horticulture and biotechnology.
Environmental Influences on Red Color Expression
Environmental influences play a significant role in the red color expression of Japanese Four O’clock plants.
The following factors impact the red color expression:
- Light Intensity: Higher light intensity enhances red coloration.
- Temperature: Cooler temperatures promote more intense red pigmentation.
- Nutrient Availability: Adequate nutrients, especially phosphorus, support vibrant red coloration.
- Moisture Levels: Balanced moisture levels help maintain optimal red color expression.
- Genetic Variability: Variations in genetic makeup influence the plant’s ability to express red pigmentation under different environmental conditions.
Understanding the interplay of these environmental factors is crucial for harnessing the full potential of red color expression in Japanese Four O’clock plants, offering opportunities for innovative approaches in cultivation and breeding.
Evolutionary Significance of Incomplete Red Color
The incomplete red coloration in Japanese Four O’clock plants may have evolutionary significance, indicating potential adaptations to specific ecological niches.
This incomplete red coloration could be a result of selective pressures favoring this trait due to its advantages in specific environmental conditions.
The table below provides a comparison of complete and incomplete red coloration in Japanese Four O’clock plants, highlighting their potential evolutionary implications:
| Aspects | Complete Red Coloration | Incomplete Red Coloration |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Benefits | Attracts pollinators | Partial camouflage |
| Ecological Niche | Open, sunny habitats | Shaded or mixed habitats |
| Genetic Variation | Less diverse | Greater diversity |
| Evolutionary Advantage | Specific pollinator attraction | Enhanced survival in diverse habitats |
Conclusion
The incomplete red coloration in Japanese four o’clock plants is a fascinating and enigmatic phenomenon that adds an element of mystery and allure to these botanical specimens.
The interplay of genetic and environmental factors leading to this unique pigmentation serves as a testament to the intricate and awe-inspiring complexity of nature.
The captivating beauty of these plants, with their incompletely red petals, is a reminder of the boundless wonders that the natural world has to offer.